Windows Boot Process
Objective: Understand the internal steps that take place when a Windows machine powers on, leading up to the execution of user-level processes like
explorer.exe.
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Boot Sequence Overview
- 3 1. BIOS or UEFI Firmware
- 4 2. Boot Manager (bootmgr)
- 5 3. OS Loader (winload.exe)
- 6 4. Kernel Initialization (ntoskrnl.exe)
- 7 5. Session Manager Subsystem (smss.exe)
- 8 6. Windows Initialization (wininit.exe)
- 9 7. User Logon & Shell Startup
- 10 Summary: Boot Flow Timeline
- 11 Advanced Tips
Introduction
The Windows boot process involves several tightly coordinated stages that transition from firmware-level initialization (BIOS/UEFI) to the full-blown execution of the Windows operating system. Each phase has a critical role in preparing the system environment, loading essential files, initializing the kernel, and finally launching user-space processes.
This knowledge is fundamental when analyzing boot-time malware, rootkits, and persistence mechanisms that abuse early stages.
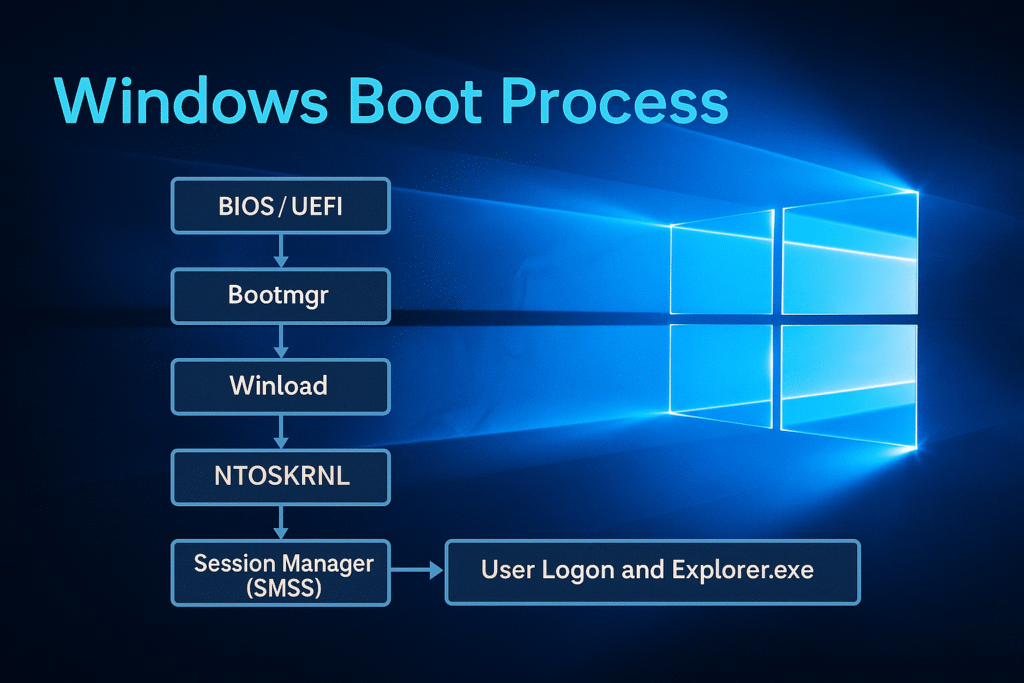
Boot Sequence Overview
Below is the high-level boot chain:
[BIOS / UEFI]
↓
[Boot Manager (bootmgr)]
↓
[Windows OS Loader (winload.exe)]
↓
[Windows Kernel (ntoskrnl.exe)]
↓
[Session Manager Subsystem (smss.exe)]
↓
[Wininit.exe / Csrss.exe / Services.exe / Winlogon.exe]
↓
[User logon and Explorer.exe startup]
Each stage is explained in detail below.
1. BIOS or UEFI Firmware
BIOS (Legacy)
- The Basic Input/Output System is firmware embedded on the motherboard.
- Initializes CPU, RAM, keyboard, and storage controllers.
- Scans for bootable devices using the boot order.
- Loads the Master Boot Record (MBR) from the first sector of the disk (LBA 0).
- MBR contains:
- Boot code (446 bytes)
- Partition table (64 bytes)
- Boot signature (2 bytes)
UEFI (Modern)
- Unified Extensible Firmware Interface replaces BIOS.
- Stores boot configuration in EFI System Partition (ESP).
- Loads
.efibinaries likebootmgfw.efidirectly from the FAT32-formatted ESP. - Supports Secure Boot and faster initialization.
Key Outcome: BIOS or UEFI hands off execution to bootmgr (via MBR or EFI).
2. Boot Manager (bootmgr)
Location:
- BIOS: Found in the root of system partition (usually
C:\) - UEFI: Located in
\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi
Responsibilities:
- Reads Boot Configuration Data (BCD) from
\Boot\BCD - Displays the boot menu (e.g., dual-boot options, recovery)
- Selects which OS to boot (if multiple)
- Loads the next-stage loader:
winload.exe
Boot Configuration Data (BCD):
- A binary registry-like file
- Contains entries for OS boot parameters
- Configurable via
bcdedit
Key Outcome: bootmgr reads BCD and transfers control to winload.exe.
3. OS Loader (winload.exe)
Location:
C:\Windows\System32\winload.exe
Responsibilities:
- Loads essential drivers and kernel images into memory:
ntoskrnl.exe(Windows kernel)hal.dll(Hardware Abstraction Layer)- Boot-start drivers (from
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services)
- Loads system registry hives into memory
- SYSTEM hive is particularly crucial
- Enables DEP, ASLR, Code Integrity (if configured)
Integrity and Security:
- Verifies digital signatures on drivers if Secure Boot is enabled
- If BitLocker is used, winload handles the decryption process
Transition:
- After successful loading, winload calls into
ntoskrnl.exe - Enters Protected Mode and switches to Kernel Mode
4. Kernel Initialization (ntoskrnl.exe)
Location:
C:\Windows\System32\ntoskrnl.exe
Responsibilities:
- Initializes kernel subsystems:
- Memory manager
- Process scheduler
- Interrupt dispatcher
- Object manager
- Security reference monitor
- Starts the Hardware Abstraction Layer (
hal.dll) - Initializes the System Service Descriptor Table (SSDT)
- Mounts the system drive using file system drivers (
ntfs.sys, etc.)
Driver Loading:
- Executes
boot-startandsystem-startdrivers (loaded from registry) - Uses
I/O managerto create device stacks
Key Transition:
- Starts the first user-mode process:
smss.exe(Session Manager)
5. Session Manager Subsystem (smss.exe)
Location:
C:\Windows\System32\smss.exe
Role:
- The first user-mode process
- Created by the kernel using
PsCreateSystemProcess
Key Tasks:
- Loads system environment variables from registry
- Launches:
- CSRSS (Client/Server Runtime Subsystem)
- WININIT (Windows Initialization Subsystem)
- Initializes the page file
- Mounts additional volumes and prepares the Winlogon environment
- Creates user sessions (Terminal Services, multi-session support)
Sessions:
- Session 0: Reserved for system services
- Session 1+: Used for interactive logon
Key Outcome: smss.exe spawns wininit.exe and csrss.exe.
6. Windows Initialization (wininit.exe)
Responsibilities:
- Starts Service Control Manager (
services.exe)- Loads all services marked as
auto-start
- Loads all services marked as
- Starts Local Security Authority (
lsass.exe)- Handles authentication and policy enforcement
- Starts Winlogon (
winlogon.exe)- Manages user logon, Ctrl+Alt+Del
- Loads GINA / Credential Providers
Csrss (Client/Server Runtime):
- Handles console windows, thread management
- Fundamental for GUI and Win32 subsystems
7. User Logon & Shell Startup
Winlogon.exe
- Displays the logon screen
- Invokes credential providers (e.g., password, PIN, smartcard)
- Upon successful authentication, calls
CreateProcessAsUserfor:
Explorer.exe
- Launches the Windows desktop, taskbar, file manager
- Runs under the user’s security token
Summary: Boot Flow Timeline
| Stage | Component | Mode | Key Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firmware Init | BIOS/UEFI | Real Mode | Hardware init |
| Bootloader | bootmgr | Protected | Loads BCD & winload |
| OS Loader | winload.exe | Real → Prot. | Loads kernel & drivers |
| Kernel Init | ntoskrnl.exe | Kernel Mode | Initializes OS subsystems |
| User Init | smss.exe | User Mode | Sets up sessions, spawns services |
| Wininit/Logon | wininit, winlogon | User Mode | Starts SCM, LSA, logon UI |
| User Shell | explorer.exe | User Mode | Loads desktop |
Advanced Tips
- Safe Mode: Modifies BCD to restrict drivers (
bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal) - Kernel Debugging: Use
bcdedit /debug onand attach WinDbg over COM or network - Boot Tracing: Use tools like Process Monitor Boot Logging, xbootmgr, or boot trace logs via Windows Performance Toolkit
- Early Launch Anti-Malware (ELAM): ELAM driver is the first AV component loaded during kernel init
It’s so important to approach gaming with knowledge, not just luck! Building skills & understanding the platform – like through resources at jiliko777 login – can really shift your perspective & promote responsible play. Great article!
Just tried out zz777br1, and gotta say, it’s pretty slick! The layout is clean, and I found some games I really dig. Definitely worth checking out, guys! Give it a go at zz777br1.
I gotta say 377betcasino’s games are fresh and frequently updated. I also notice some new slot games. Definitely recommend! Try it now 377betcasino.